Introduction
In a groundbreaking milestone that marks a leap in robotics, engineers at Columbia University have developed a robot hand that demonstrates unprecedented dexterity and sensitivity. This marvel of modern technology not only performs complex tasks but does so without the need for visual input—a capability akin to our own hands operating in the dark.
The Challenge of Robotics
Traditionally, robotic manipulators have been limited to basic ‘pick and place’ operations, with more intricate tasks remaining the domain of human hands. However, the Columbia engineers’ development challenges this paradigm, paving the way for a future where robots can perform tasks that were once thought impossible.
Innovation 1: Advanced Tactile Sensors
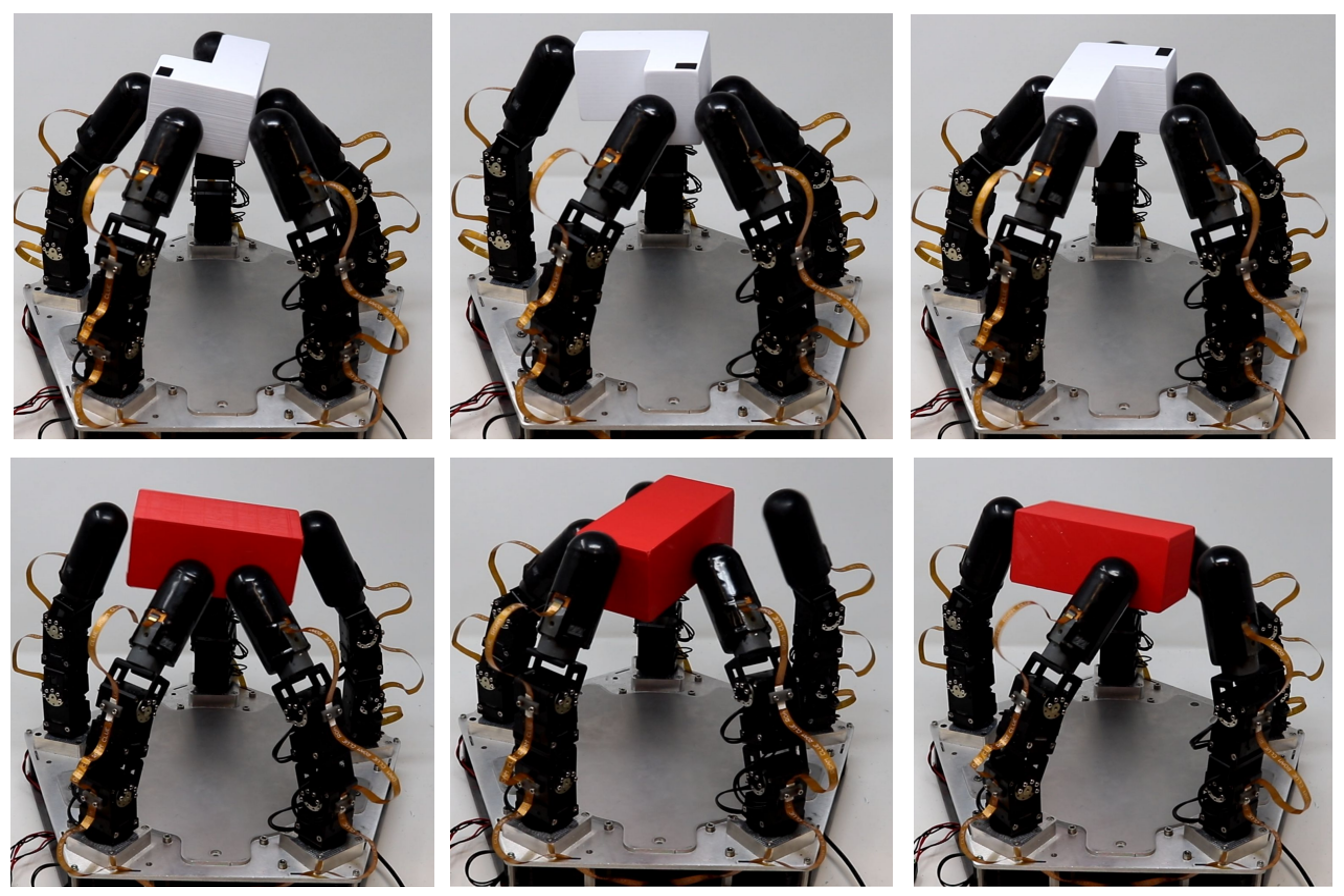
tactile robot fingers designed by the same team
The first key innovation lies in the advanced tactile sensors used by the robot hand. These sensors are optimized to detect subtle changes in texture and shape, allowing the robot to grasp objects with precision and control—even without visual feedback.
Innovation 2: Reinforcement Learning Algorithms
Application of motor learning algorithms
The second major breakthrough is the application of reinforcement learning algorithms. This machine learning approach enables the robot hand to ‘learn’ new tasks through practice, gradually refining its dexterity over time.
The Learning Process
Reinforcement learning involves a trial-and-error process where the robot hand completes approximately a year’s worth of practice in mere hours. The skills learned in this simulated environment are then transferred to real-world robotic hands, ensuring that the robot can perform tasks with remarkable efficiency and accuracy.
Implications for Various Industries
The implications of this development are far-reaching and profoundly exciting. Robots with such high levels of dexterity could revolutionize industries such as logistics, material handling, and advanced manufacturing, potentially alleviating supply chain challenges that have long been a hurdle in these sectors.
Applications Beyond the Lab
As we move toward an era where AI and robotics integrate into our daily lives, advancements like this one bring us closer to realizing scenarios where robots can perform tasks with the finesse and versatility of human hands. Imagine a robot not only understanding your command to make a sandwich but also physically performing it for you! This vision underscores the transformative potential of Columbia’s breakthrough.
Future Outlook
Despite significant progress, achieving the full dexterity and versatility of the human hand remains a distant goal. However, this development marks an important milestone, offering hope that future innovations will bring us closer to that ideal. The fusion of abstract intelligence with embodied intelligence continues to push the boundaries of what is possible in robotics.
Conclusion
The Columbia team’s highly dexterous robot hand represents a significant leap in robotics and AI, bringing us closer to a future where machines can perform tasks we have always taken for granted. As we continue to advance, one thing is clear—the future holds immense potential.
By Dr. Kevin Washington, University of Pennsylvania